The Power of Breastfeeding
The Power of Breastfeeding: Nourishing Infants, Empowering Mothers, and Fostering Healthy Societies
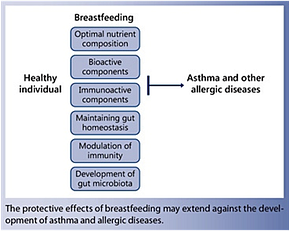
Breastfeeding is a natural and fundamental aspect of human existence, providing optimal nutrition and numerous health benefits to infants. For millennia, breastfeeding has been the primary method of nourishing newborns, ensuring their growth, immunity, and cognitive development.
The importance of colostrum for newborn children
Colostrum is the first milk produced by the mother’s mammary glands during the initial days after giving birth. It is a thick, yellowish, and nutrient-rich fluid that differs in composition from mature breast milk. Colostrum is often referred to as “liquid gold” due to its extraordinary health benefits and importance for new-borns

Reasons why colostrum is so crucial for the health and well-being of newborns:
- Immune Protection: Colostrum is packed with antibodies, immune cells, and other essential components that give the baby passive immunity. These immune factors help protect the newborn against a wide range of infections and diseases during the vulnerable early days of life when the baby’s own immune system is still developing.

2. Easy Digestibility: Colostrum is easily digestible by the newborn’s immature digestive system. Its concentrated nutrient content gives the baby all the essential nutrition needed in small, manageable volumes.
3. Laxative Effect: Colostrum acts as a natural laxative, helping the baby pass meconium, the thick dark stool accumulated in the intestines during fetal life. This aids in the elimination of waste products from the baby’s body.
4. Gut Health: Colostrum contains high levels of beneficial bacteria, known as probiotics, which support the establishment of a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for the baby’s digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall immune function.
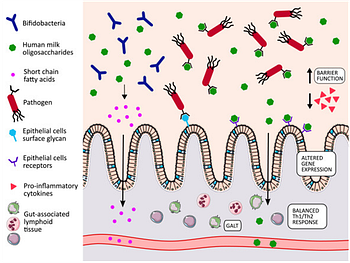
5. Growth Factors: Colostrum contains various growth factors that promote the development and maturation of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, enabling efficient nutrient absorption.
6. Brain Development: Colostrum contains important nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and choline, which are crucial for brain development and cognitive function in the early stages of life.
7. Anti-inflammatory Properties: Colostrum has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe and protect the baby’s delicate tissues, reducing the risk of inflammation-related. conditions.
8. Hormonal Regulation: Colostrum contains hormones that support various physiological processes in the newborn, including metabolic regulation and adaptation to the outside environment.
9. Emotional Bonding: Breastfeeding colostrum fosters the emotional bond between mother and baby, promoting feelings of comfort and security for the infant.

10. Preparing the Gut: Colostrum helps prepare the baby’s gut for the subsequent transition to mature breast milk, which occurs a few days after birth. The transition is gradual, allowing the baby’s digestive system to adapt to the changes in breast milk composition.
Given its rich nutrient content and potent immune-boosting properties, colostrum plays a vital role in jumpstarting the baby’s health and providing the foundation for a strong immune system. Breastfeeding colostrum in the early postpartum days is essential for maximizing the health benefits it offers. Mothers are encouraged to initiate breastfeeding as soon as possible after birth to ensure that their newborns receive this vital and nourishing liquid gold.
Benefits of Breast Milk to the Infant:
- Optimal Nutrition: Breast milk provides the perfect balance of nutrients tailored to the baby’s specific developmental needs, supporting healthy growth and development.

2. Enhanced Immune Protection: The antibodies and white blood cells in breast milk help protect the baby against infections and illnesses, reducing the risk of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections
3. Cognitive Development: The presence of essential fatty acids, such as DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), in breast milk supports brain development and cognitive function.
4. Reduced Allergy Risk: Breast milk contains factors that may help reduce the risk of allergies and sensitivities in the baby.
5. Digestive Health: Breast milk is easily digestible, reducing the likelihood of digestive discomfort and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
6. Bonding and Emotional Health: Breastfeeding fosters a strong emotional bond between mother and baby, promoting feelings of comfort and security for the infant.
7. Long-Term Health Benefits: Breastfeeding has been associated with reduced risks of chronic diseases later in life, such as obesity, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Maternal health advantages of breastfeeding:

Breastfeeding offers several maternal health advantages, providing numerous benefits to mothers during both the postpartum period and beyond. Here are some of the key benefits of breastfeeding for mothers:

1. Faster Postpartum Recovery: Breastfeeding triggers the release of oxytocin, which helps the uterus contract, reducing postpartum bleeding and aiding in the recovery process.
2. Weight Loss: Breastfeeding can help mothers lose pregnancy weight more effectively by burning extra calories to produce breast milk.
3. Reduced Risk of Postpartum Depression: Breastfeeding is associated with a reduced risk of postpartum depression. The act of breastfeeding and the bonding it fosters can positively impact maternal mental health.

4. Lower Risk of Certain Cancers: Breastfeeding has been linked to a reduced risk of breast and ovarian cancers in mothers.

5. Bone Health: Lactation can lead to increased bone density, which may help protect against osteoporosis later in life.
6. Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Breastfeeding is associated with a decreased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in mothers.

7. Natural Contraceptive Effect: Exclusive breastfeeding, known as the Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM), can act as a natural form of contraception, providing some protection against pregnancy during the first six months after childbirth.
8. Emotional Bonding: Breastfeeding fosters a close emotional bond between the mother and the baby, promoting feelings of comfort, love, and connection.

9. Convenience and Cost-Effectiveness: Breast milk is always available, at the right temperature, and requires no preparation or cost, unlike formula feeding.
10. Decreased Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Some studies suggest that breastfeeding may lower the risk of cardiovascular disease in mothers.

11. Lowered Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: Breastfeeding has been associated with a decreased risk of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
12. Delayed Return of Menstruation: In many cases, breastfeeding delays the return of menstruation, providing a temporary break from monthly periods.
Breastfeeding offers numerous health benefits for both the baby and the mother and is recommended by major health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), as the best source of nutrition for infants during their first six months of life and beyond.

Promoting breastfeeding through education and awareness requires collaboration among healthcare institutions, government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community leaders, and educational institutions. A comprehensive approach that addresses cultural diversity, individual needs, and challenges can contribute to higher breastfeeding rates and better health outcomes for both mothers and infants.

Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
площадка для продажи аккаунтов услуги по продаже аккаунтов
услуги по продаже аккаунтов магазин аккаунтов социальных сетей
купить аккаунт безопасная сделка аккаунтов
платформа для покупки аккаунтов площадка для продажи аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов аккаунт для рекламы
продать аккаунт купить аккаунт с прокачкой
магазин аккаунтов магазин аккаунтов
Account Purchase Account Sale
Account Sale Profitable Account Sales
Guaranteed Accounts Account Buying Service
Account Catalog Account market
Accounts for Sale Account marketplace
Buy Pre-made Account Buy and Sell Accounts
Database of Accounts for Sale Account Sale
Account exchange Account Selling Platform
Account market Account Buying Service
Account market Sell accounts
Buy accounts Accounts for Sale
account buying service profitable account sales
account trading platform buy account
account trading account exchange service
accounts marketplace guaranteed accounts
buy accounts buy accounts
secure account purchasing platform website for buying accounts
website for buying accounts marketplace for ready-made accounts
secure account sales account trading platform
account store gaming account marketplace
buy accounts accounts for sale
account exchange account sale
account purchase accounts market
profitable account sales online account store
online account store accounts for sale
website for buying accounts online account store
secure account sales account exchange service
account marketplace account market
account catalog buy account
profitable account sales account market
buy account account buying service
buy account purchase ready-made accounts
account marketplace accounts for sale
website for buying accounts sell pre-made account
accounts marketplace account market
accounts market ready-made accounts for sale
marketplace for ready-made accounts guaranteed accounts
find accounts for sale accounts market
sell account https://accounts-offer.org
online account store https://accounts-marketplace.xyz
database of accounts for sale https://buy-best-accounts.org
verified accounts for sale https://social-accounts-marketplaces.live/
accounts market accounts marketplace
account trading platform https://social-accounts-marketplace.xyz
social media account marketplace https://buy-accounts.space
account trading platform https://buy-accounts-shop.pro
sell account https://social-accounts-marketplace.live
account sale https://buy-accounts.live
account exchange https://accounts-marketplace.online
account trading service https://accounts-marketplace-best.pro
биржа аккаунтов https://akkaunty-na-prodazhu.pro
магазин аккаунтов rynok-akkauntov.top
маркетплейс аккаунтов kupit-akkaunt.xyz
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
магазин аккаунтов купить аккаунт
купить аккаунт https://akkaunty-market.live/
продажа аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunty-market.xyz/
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей https://akkaunty-optom.live
продажа аккаунтов магазины аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей akkaunty-dlya-prodazhi.pro
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей https://kupit-akkaunt.online/
facebook ad account buy buy account facebook ads
buying fb accounts fb account for sale
buying facebook accounts https://buy-ad-account.top
facebook ads accounts https://buy-ads-account.click
buy aged fb account https://ad-account-buy.top
buy aged fb account https://buy-ads-account.work
facebook accounts for sale buy ad account facebook
buy facebook profile facebook ad account buy
buy ad account facebook https://ad-accounts-for-sale.work
google ads account buy https://buy-ads-account.top
google ads account for sale https://buy-ads-accounts.click/
facebook account sale buy facebook accounts
buy google ads accounts https://ads-account-for-sale.top/
old google ads account for sale https://ads-account-buy.work
sell google ads account https://buy-ads-invoice-account.top
buy google adwords account https://buy-account-ads.work/
buy google adwords account buy aged google ads account
buy aged google ads accounts https://sell-ads-account.click
buy google ad threshold account https://ads-agency-account-buy.click
verified bm https://buy-business-manager.org/
buy google ads verified account buy google ads threshold accounts
facebook bm for sale https://buy-bm-account.org/
buy fb business manager buy-business-manager-acc.org
verified business manager for sale https://buy-verified-business-manager-account.org
buy facebook bm account buy-verified-business-manager.org
buy fb bm https://business-manager-for-sale.org
buy facebook business manager verified buy facebook business manager verified
facebook business account for sale https://buy-bm.org
buy verified business manager facebook buy business manager facebook
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/ka-GE/join?ref=RQUR4BEO
buy verified facebook buy-business-manager-accounts.org
tiktok ads account for sale https://buy-tiktok-ads-account.org
buy tiktok ads account https://tiktok-ads-account-buy.org
tiktok ads account buy https://tiktok-ads-account-for-sale.org
tiktok ads account buy https://tiktok-agency-account-for-sale.org
tiktok ads agency account https://buy-tiktok-ad-account.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://buy-tiktok-ads-accounts.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://buy-tiktok-ads.org
buy tiktok ad account https://buy-tiktok-business-account.org
tiktok agency account for sale https://tiktok-ads-agency-account.org
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.